

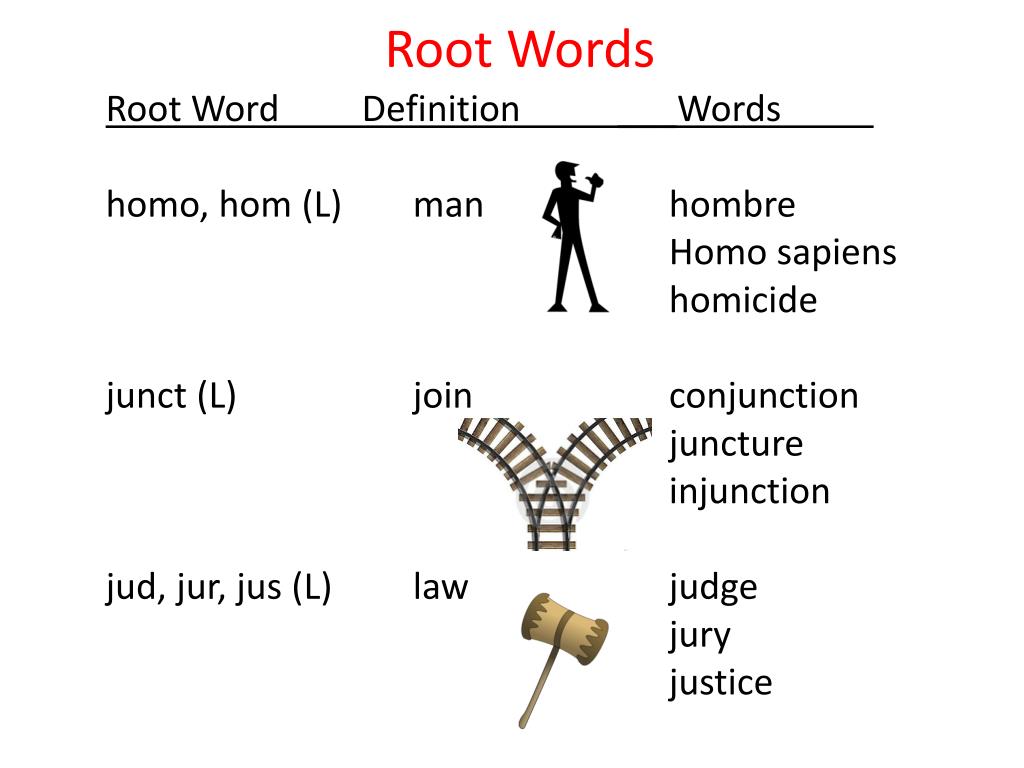
The meaning of a word can be easily determined if one knows the root word. In words that have two or more syllables, there is a root word and two or more prefixes or suffixes. It may come from several different languages like Greek and Latin.Īffixes are usually added to root words in order to create new words. It is the term that a certain word comes from originally and is a word’s basic linguistic unit.
ROOT WORD VS WORD ROOT FREE
Free morphemes are words that can stand alone or that can appear with other words while bound morphemes are prefixes and suffixes that appear with other morphemes to form a word.Ī root word may be a word that has a meaning or one that does not have a meaning. When combined with other words, it can form new words that may or may not have similar meanings as the original word which can either be a root word or a base word.Ī root word is the primary form of a word which can either be free morphemes or bound morphemes. In its simplest form, it can have a definite meaning. Knowing the various verb forms is a great starting point for learning these complex rules and exceptions.A word can be simple or complex. However, with others, they are all different (e.g., take, I took, I had taken). Understanding the verb forms (including the root form) is essential when learning English because it allows teachers and pupils to talk about the components that form the various tenses.įor example, with some verbs, the root form, past form, and past participle form are the same (e.g., let, I let, I had let). The "-ING form" is also known as the "present participle form.".The "past form" is also known as the "past-tense form.".The "-S form" is also known as the "third-person singular present-tense form.".The "verb root" is also known as the "base form" or the "uninflected form.".The table below shows the five verb forms in English.īear in mind that you might encounter other names for these verb forms.

Saddam Hussein systematically violated every UN resolution that demanded he disarm and destroy his chemical and biological weapons.The verb root of a verb appears in the subjunctive mood. Next time I see you, remind me not to talk to you.Eat a live toad the first thing in the morning and nothing worse will happen to you the rest of the day.The verb root is used for commands (i.e., the imperative mood. Verb Roots in the Imperative Mood (i.e., Commands) The verb root appears in all versions of the present tense except the third person singular (shaded red). Note that the past form of the verb "to drink" is not the same as the past-participle form.)
(This is used to make these forms: drinks, drank, drinking, drunk. (This is used to make these forms: thinks, thought, thinking.) (This is used to make these forms: lives, lived, living.) (This is used to make these forms: plays, played, playing.) Note that watched is both the past form and the past-participle form. (The verb root "watch" is used to make these three forms: watches, watched, watching. The verb root is always used to create the other forms of regular verbs (i.e., verbs that comply with the normal rules for creating the various forms) but not necessarily for irregular verbs (i.e., verbs that do not comply with the normal rules). The verb root is used to create the other forms of the verb.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
